What Is AIF? What Are The Types of AIF?
In the dynamic landscape of financial markets, investors are constantly seeking avenues that offer diversification and attractive returns beyond traditional investment options. One such domain that has gained prominence is Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs). AIFs are investment vehicles that pool funds from investors to invest in a variety of asset classes, going beyond conventional stocks and bonds. In this blog, we will delve into the intriguing world of AIFs, exploring their definition, significance, and the three distinct types of AIF categories they fall under.
What is Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs):
Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) are pooled investment vehicles that collect funds from investors, whether individuals or institutions, to invest in assets beyond traditional stocks and bonds. AIFs offer diversification and access to various asset classes such as real estate, private equity, hedge funds, and commodities. They are regulated by securities regulators in many jurisdictions and are managed by professional fund managers. AIFs often cater to sophisticated investors seeking higher returns or unique investment opportunities not typically available through conventional investment avenues.
Types of AIF:
The types of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) can be broadly categorized into three categories based on their investment strategies and objectives:
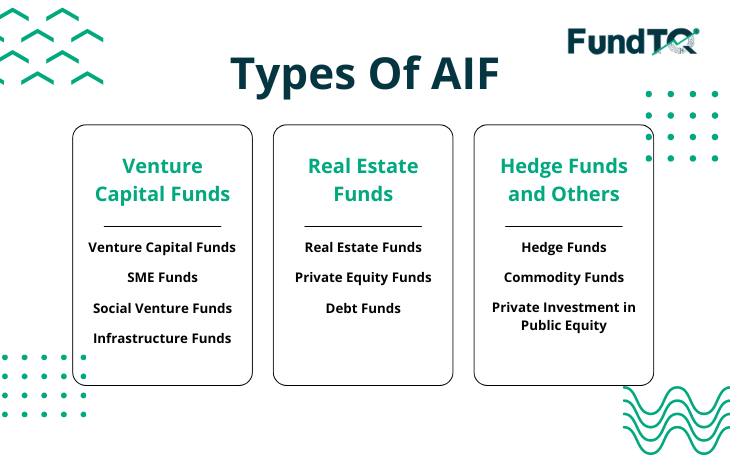
Type 1: Venture Capital Funds
Following are the types of Venture Capital Funds:
1. Venture Capital Funds
Venture Capital Funds are AIFs that focus on investing in startups and early-stage companies with high growth potential. These funds provide capital to fuel innovation, support entrepreneurship, and generate returns by participating in the success of these ventures.
2. SME Funds
SME Funds target small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These funds aim to provide financial support and guidance to SMEs, fostering their growth and expansion. By investing in SMEs, these funds contribute to job creation and economic development.
3. Social Venture Funds
Social Venture Funds combine financial returns with social impact. These AIFs invest in businesses that address social and environmental challenges. By aligning financial goals with societal benefits, social venture funds play a crucial role in promoting sustainable and responsible investing.
4. Infrastructure Funds
Infrastructure Funds focus on investing in physical assets like roads, bridges, energy projects, and other essential infrastructure. These funds provide long-term capital to support the development and maintenance of critical infrastructure projects.
Category 2: Real Estate Funds
Following are the types of Real Estate Funds:
1. Real Estate Funds
Real Estate Funds invest in various real estate projects, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties. Investors benefit from the potential appreciation of property values and rental income, making real estate funds an attractive option for diversification.
2. Private Equity Funds
Private Equity Funds invest in privately held companies. These funds acquire significant ownership stakes in companies with the aim of improving operations, enhancing value, and eventually exiting through strategies like IPOs or mergers and acquisitions.
3. Debt Funds
Debt Funds focus on fixed-income securities and debt instruments. Investors in debt funds receive regular interest payments, providing a stable income stream. These funds are considered lower risk compared to equity-focused alternatives.
Category 3: Hedge Funds and Others
Following are the types of Hedge Funds And Others:
1. Hedge Funds
Hedge Funds employ various strategies, including leverage and derivatives, to generate returns. These funds are known for their flexibility in asset allocation and risk management, making them suitable for sophisticated investors seeking alternative investment strategies.
2. Commodity Funds
Commodity Funds invest in commodities like gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products. These funds provide investors exposure to the price movements of physical commodities, allowing for diversification beyond traditional asset classes.
3. Private Investment in Public Equity (PIPE)
PIPE Funds invest in publicly traded companies by purchasing newly issued shares directly from the company. This form of private investment allows companies to raise capital without going through traditional public offerings.
Conclusion
Alternate Investment Funds play a pivotal role in providing investors with diverse investment opportunities, catering to various risk profiles and investment objectives. Whether it’s supporting startups, fostering social impact, or participating in real estate and hedge fund strategies, AIFs offer a rich tapestry of options for those looking to go beyond traditional investments. As with any investment, it’s essential for investors to conduct thorough research, understand the risks involved, and align their investment choices with their financial goals. In the ever-evolving world of finance, AIFs stand as a testament to the innovation and adaptability of investment strategies.
Also Read: Angel Investors vs Venture Capital

