Financial Modeling Explained: The Complete Guide for Beginners & Professionals
Have you ever been asking yourself, What is financial modeling? you are in the right place. Financial modeling is an important skill in finance, investment, entrepreneurship, and any other person who wants to make financial decisions based on data. With this all-in-one guide, you will dissect all information you need to know about financial modeling- starting with the basics, up to advanced concepts and on a step by step basis.
What is Financial Modeling?
One of the most prizes though least comprehended skills in financial analysis is financial modeling. Financial modeling aims at integrating accounting, finance, and business metrics in order to make a forecast about future outcomes of the business.
A financial model is plainly speaking a spreadsheet typically developed in Microsoft Excel, which predicts the financial performance of a business over an extended period. The projection is usually made on the past performance of the company, as well as the assumptions with respect to the future and needs creation of an income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and supportive schedules (one of many types of approaches to financial statement modeling).
It is possible to develop more sophisticated models based on it such as discounted cash flow analysis (DCF model), leveraged buyout (LBO), mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and sensitivity analysis. An illustration of a financial modelling in Excel is provided below:
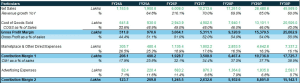
Core Highlights
– What is Financial modelling: It is a combination of accounting, finance and business metrics to develop a projection on the future outcome of a company.
– Financial modeling is mainly aimed at accurately modeling the future of a company in terms of financial performance.
– Modelling can be applied in valuing firms, in establishing whether to raise capital or to expand the business through acquisitions or organic growth.
What Is the Purpose of a Financial Model and How Is It Used?
Financial models are of numerous types and have a broad variety of applications. A financial model is applied to the output to use in decision-making and conducting a financial analysis, both internally and externally. Decisions are made using financial models regarding:
- Capital raising (debt and/or equity).
- Acquisitions (businesses and /or assets)
- Expanding the business in-house (i.e. new stores, new markets, etc.).
- Disposing of the assets and business units.
- Budgeting and forecasting (planning the future years)
- Capital investment (what projects to invest in priority)
- Valuing a business
- Ratio analysis/ financial statement analysis.
- Management accounting
Types of Financial Models
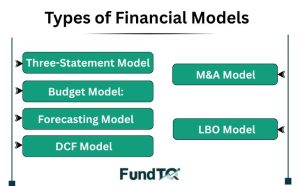
It is important to understand various types of financial models to be able to apply them. In the most frequent forms it is:
- Three-Statement Model: Combines income, balance, and cash flow statements.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model: This is a model applied in valuation, which relies on anticipated cash flow and discount rates.
- Merger and Acquisition (M&A) Model: This is an analysis of the financial effect of a merger or acquisition.
- Budget Model: Assists firms in projecting income and expense.
- Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model: It is the acquisition financing that is based on the debt financing.
- Forecasting Model: Estimating future revenue, costs and other significant measures of the project.
Steps to Build a Financial Model – Simple Way
Financial modeling is an important financial skill among finance practitioners, investors and business analysts. A properly designed model facilitates decision-making, valuation, budgeting as well as analysis of investments. These steps are to be followed in order to develop a trustworthy and precise financial model.
1. Define the Objective
Defining the purpose of the financial model is important before creating it. Is it designed to be business valued, budgeted, forecasted or an investment analysis tool? The purpose defines how your model will be written, how detailed it will be and what kind of products it will give. Having a goal is a way of keeping your model focused and actionable.
2. Collect Historical Data
Prepare full historical financial statements, that is, income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) including revenue growth, gross margins, operating expenses, and capital expenditures. The basis of your model is made by accurate historical data, and enhances the reliability of forecasting.
3. Make Assumptions
Make real and information-based assumptions about your model, such as:
- Revenue growth rates
- Cost projections
- Capital expenditures (CapEx)
- The interest rates and financing costs.
Write clearly on what you assume, with reference where necessary. Clear assumptions make the difference between credibility and enable other people to comprehend and believe in your model.
Learn about: Financial Model for BPO Company
4. Design the Model
Develop a logical structure of your financial model:
- Inputs: History and assumptions.
- Formulas and projections: Calculations.
- Outputs: Critical results, measures, and graphics.
Be clean in layout, colour coding and standard formatting. An effective model enhances usability and minimise errors and makes it easier to be reviewed by other people.
5. Forecast Financial Statements
Prepare the main financial statements according to your assumptions:
- Income Statement: Revenue, costs and net profit.
- Balance Sheet: Assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Cash Flow Statement: operating, investing and financing.
Make your forecasts coherent and interrelated. Any modification in assumptions ought to automatically update all statements.
6. Perform Analysis
Discuss the implications of your model:
- Financial ratios: The profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and leverage ratios.
- Scenario analysis: best-case, worst-case and base-case scenarios.
- Sensitivity analysis: Evaluate the effect of variation in assumptions.
This is done to determine the risks, opportunities and the key drivers of values.
7. Review & Validate
Check the accuracy and logical consistency of your model:
- Check formulas and calculations.
- Compare past statistics with real statements.
- Make sure that the assumptions are fair and fair.
It involves peer review or external validation which provides extra credibility.
Pro Tip: Maintain Transparency
Trust is essential in your financial model, and transparency is the key to it. Clarify assumptions, sources, and methodology in a clear manner in order to make stakeholders recognise the importance of your analysis. Not only that increases the confidence in your conclusions but also increases your professional credibility.

Tools for Financial Modeling
While Excel remains the most popular tool, other software enhances modeling efficiency:
- Microsoft Excel
- Google Sheets
- Specialised Tools
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-complicating formulas
- Ignoring historical trends
- Based on impractical assumptions.
- Lack of conducting scenario analysis.
- Failing to update the model on a regular basis.
Note: All financial models are as good as the assumptions and data on which they are based.
Bottom Line
Financial modeling is an effective tool that enables the professionals to make quality financial decisions. Learning about its forms, elements, and optimal practices, both novices and specialists can utilize the potential of financial data to the fullest extent.
Financial modeling is the backbone of modern finance whether you are predicting revenue, valuing a business or looking into the investments. Begin training nowadays, and convert raw data into strategic knowledge.




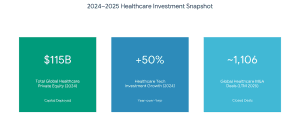 What is Healthcare Investment Banking?
What is Healthcare Investment Banking?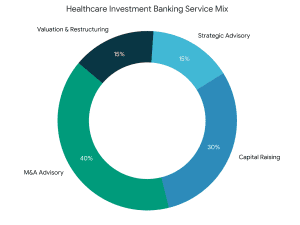 Life sciences investment banking provides a varied area of services. Key services include:
Life sciences investment banking provides a varied area of services. Key services include: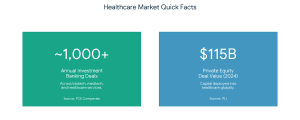



 What is Investment Banking Services?
What is Investment Banking Services?
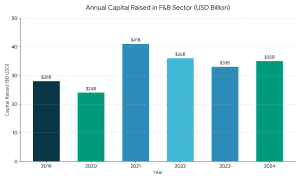
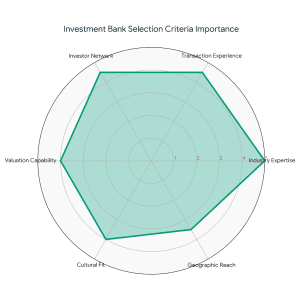
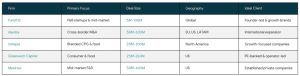


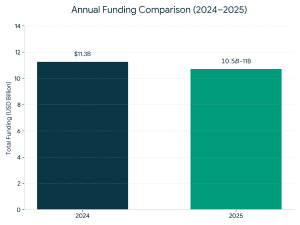 This is a full guide on how to navigate the startup funding in India in 2025 – 2026.
This is a full guide on how to navigate the startup funding in India in 2025 – 2026. 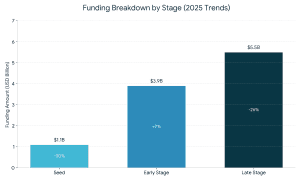 The various funding routes also have trade offs, in matters of control, risk, and scalability, and those entrepreneurs must match them to their business model.
The various funding routes also have trade offs, in matters of control, risk, and scalability, and those entrepreneurs must match them to their business model.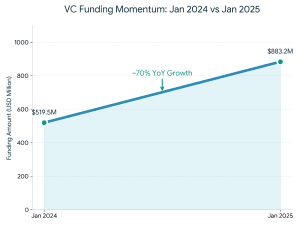
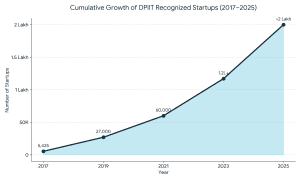 These are the main trends that are going to impact the funding this year:
These are the main trends that are going to impact the funding this year:



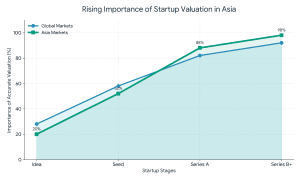
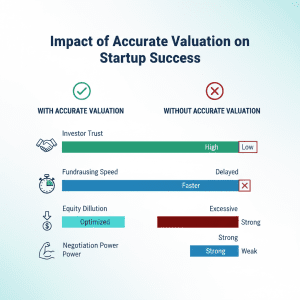
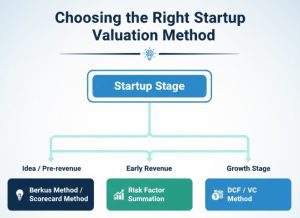


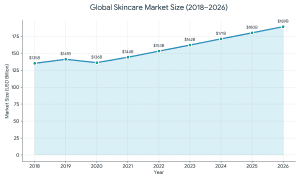
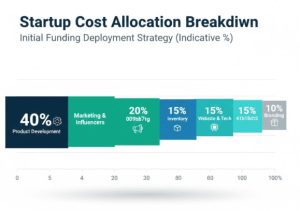 I give this a rough breakdown:
I give this a rough breakdown: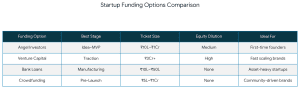 As a beauty founder, you’re not limited to a single funding route. Here are some options to explore:
As a beauty founder, you’re not limited to a single funding route. Here are some options to explore: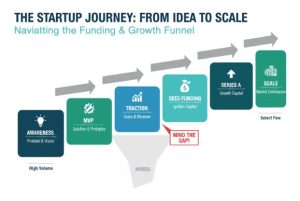 The pitch is a decisive part in your funding process.
The pitch is a decisive part in your funding process.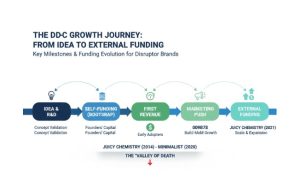 Pros:
Pros: