Proven Ways to Secure Investment for Battery Recycling Projects
Battery recycling is one of the most appealing cleantech opportunities today as the world is transitioning to electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and circular economies. Scaling up of recycling operation is however expensive in terms of capital, cutting-edge technology and right investors. Whether you are looking to raise funding to start a battery recycling business, this guide can help find out who to consider, how to make the pitch, and how to find capital – which could be an angel investor or venture capital, or private equity.
What Is Funding for a Battery Recycling Startup?
Funding of a battery recycling startup Capital raised to develop, scale, or commercialize technologies to recover valuable materials (lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese) in used batteries.
The funding is usually in support of:
- Technology development and pilot plants.
- Infrastructure collection and logistics.
- Environmental permits and regulatory compliance.
- Processing facilities on a commercial scale.
- Current assets and human resources.
Why Battery Recycling Startups Are Attracting Investors
Recycling of batteries is no longer a niche concept; it is a strategic requirement.
The Major Investor Drivers.
- Critical shortage of critical minerals.
- Mandates of government sustainability.
- Quick EV and energy storage implementation.
- Reduced carbon footprint compared to mining.
- Recovered materials of high margin.
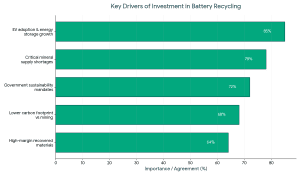 Consequently, the investment in battery recycling startups has taken precedence in clean-tech centric funds and ESG investors, as well as industry actors with a strategic agenda.
Consequently, the investment in battery recycling startups has taken precedence in clean-tech centric funds and ESG investors, as well as industry actors with a strategic agenda.

Types of Funding for Battery Recycling Startups
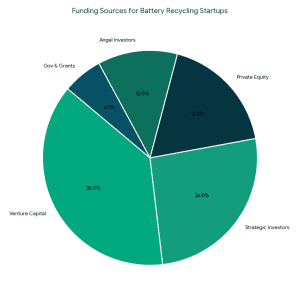 1. Angel Investors for Battery Recycling
1. Angel Investors for Battery Recycling
Angel investors normally invest in early-stage ventures with outstanding technical resources and a definite commercialization abilities.
Best fit for:
- Pre-seed and seed stages
- Pilot projects
- Proprietary recycling technologies.
- Seek experienced angels who have experience in:
- Clean energy
- Advanced manufacturing
- Materials science
This round frequently coincides with early accelerators and startup funding.
2. Venture Capital for Battery Recycling
Battery recycling venture capital targets transformative technologies that have global market opportunities.
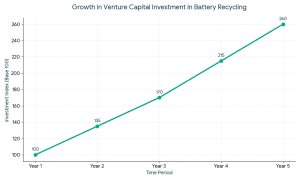 VCs typically invest when:
VCs typically invest when:
- The technology is validated
- Unit economics are proven
- There’s a clear path to scale
- VC firms often evaluate:
- IP defensibility
- Strategy of sourcing feedstock.
- Long term offtake contracts.
When you intend to raise Series A funding, you should have airtight traction, revenue model, and scalability story.
3. Private Equity Battery Recycling Investment
Investors In PEBs concentrate on later-stage businesses or businesses with high assets.
Ideal for:
- Commercial-scale plants
- Expansion capital
- M&A-driven growth
PE firms prioritize:
- Stable cash flows
- Established operational efficiency.
- Long-term supply contracts
This type of battery recycling business financing is optimal when your company can be predictable in revenue.
4. Cleantech & Strategic Investors
Recycling of battery startups by Cleantech battery investors typically entail:
- Automotive OEMs
- Battery manufacturers
- Mining and material companies.
They do not only invest to get returns but they also invest to secure supply chains.
Strategic investors are able to offer:
- Guaranteed feedstock
- Long-term buy contracts.
- Technical partnerships
Best Investors for Battery Recycling Startups
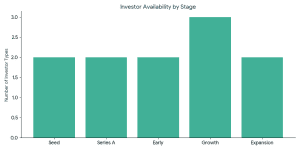 The ideal investors in battery recycling startups usually have the following characteristics:
The ideal investors in battery recycling startups usually have the following characteristics:
- Extensive knowledge on sustainability economics.
- Long-term capital horizon
- Specialization in operation within an industry.
Types of investors to target:
- Climate-focused VC funds
- ESG private equity firms
- Industrial strategic investors.
- Specialized green funds
Proven Ways to Secure Investment for Battery Recycling Projects
1. Build a Compelling Investment Narrative
Investors do not simply invest in technology, but they invest in vision and implementation.
Your story must answer clearly:
- What problem are you solving?
- What is special about your solution compared to other solutions?
- What is the profitability of your model?
Powerful stories work well when they are backed up with good business valuation calculator reports and with realistic financial assumptions.
2. Prepare an Investor-Ready Pitch Deck
Your pitch deck must be concise, data-backed, and outcome-focused.
Key slides to include:
- Drivers of market size and demand.
- Technology differentiation
- Revenue model
- Unit economics
- Regulatory advantage
It is better to use professional pitch deck templates or free pitch deck templates which will ensure that your presentation aligns with what the investors expect.
3. Demonstrate Commercial Viability Early
The investors in battery recycling are demanding.
Ways to show traction:
- Signed MOUs or LOIs
- Pilot plant performance data.
- Strategic partnerships
- Government approvals
This goes a long way in enhancing access to battery recycling startups at superior valuations.
4. Leverage Investment Banking & Advisory Support
Expert advisors assist you:
- Find the appropriate investor mix.
- Hybrid funding or structured equity.
- Position your firm at the right place.
The early use of investment banking services may help to minimize dilution and shorten fundraising timelines.
5. Optimize for Regional Funding Ecosystems
In case you are operating in emerging markets, access to fundraising of startups in India or other regional ecosystems can open:
- Government-backed capital
- Sustainability-linked funding
- Home-based strategic investors.
This strategy serves as an addition to larger start-up fundraising efforts in the world.
How Much Capital Does a Battery Recycling Startup Need?
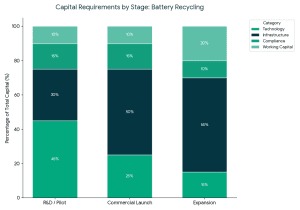 Capital requirements vary by stage:
Capital requirements vary by stage:
|
Stage |
Typical Capital Range |
|
R&D / Pilot |
Low to mid seven figures |
|
Commercial Launch |
Mid to high eight figures |
| Expansion |
Nine figures+ |
Accessing the right capital for battery recycling startup depends on aligning the funding stage with investor expectations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Raising Battery Recycling Startup Funding
- Expert projection of short-term margins.
- Disregard of regulatory schedules.
- Poor sourcing of feedstock.
- Poor cost modeling
- Reaching off-centered investors.
By not falling into these traps, it enhances success rates in battery recycling startup investors talks.
Final Thoughts:
Finding the capital to finance battery recycling startup ventures is no longer a matter of money but one of selecting investors with technology, regulation and long-term sustainability economics knowledge.
Founders who combine:
- Strong execution
- Clear financial discipline
- Strategic alignment between investors.
are the ones that are constructing the future of profitable, scalable battery recycling companies. When you are going to raise startup funding, plan early, position, and take fund raising as a long-term relationship and not a transaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I get funding for a battery recycling startup?
To fund a battery recycling company, you would go to angel investors, venture capital companies, cleantech funds or strategic players in the industry once you have proven your technology, unit economics, and supply chain.
2. What investors are interested in battery recycling startups?
Investors at Battery recycling startups are generally cleantech VCs, and private equity funds, as well as angel investors, ESG funds, and strategic Investors like battery manufacturers and EV companies.
3. Is venture capital suitable for battery recycling startups?
Yes, battery recycling venture capital fits start-ups that have a scalable technology, defensible IP, and a road to commercial production and profitability.
4. How much capital does a battery recycling startup need?
The initial capital requirements of a battery recycling business start-up are dependent on the size -pilot projects require less capital investment, whereas commercial plants need considerably more capital investment due to the infrastructure and compliance expenses.
5. What do investors look for in battery recycling business funding?
When investing in the battery recycling business, investors consider efficiency in technology, regulatory preparedness, the availability of feedstock, margins on recovered materials, and sustainable demand.

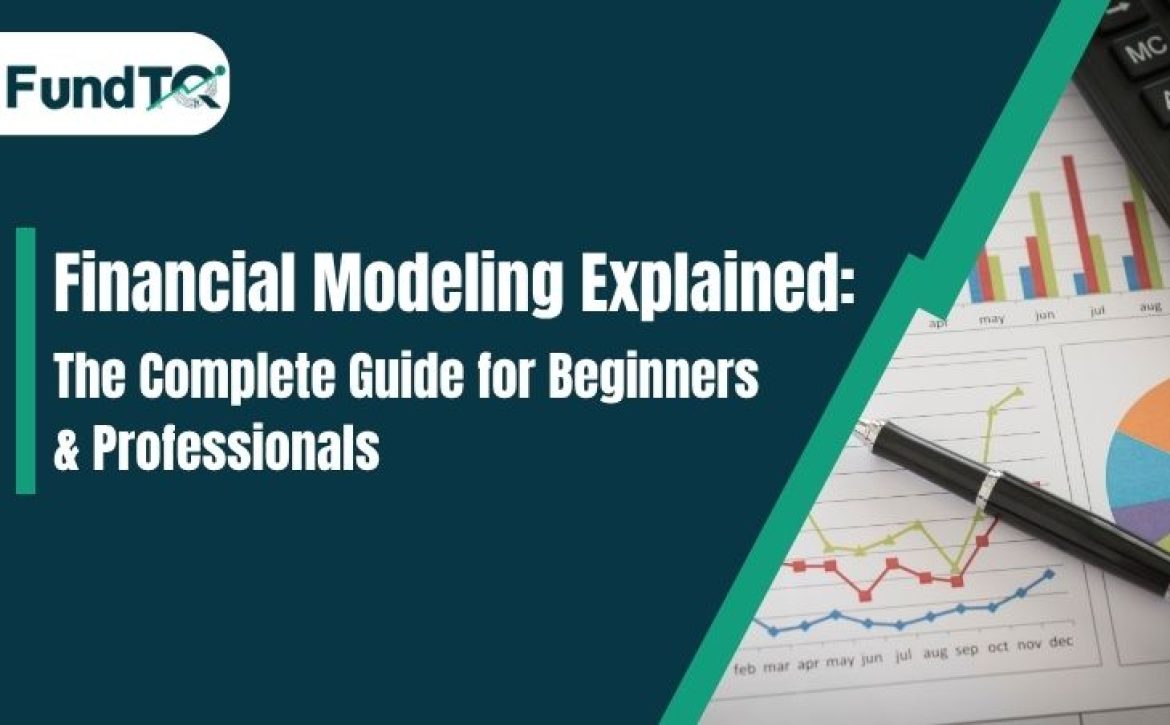
 Waste Management Financial Model
Waste Management Financial Model 



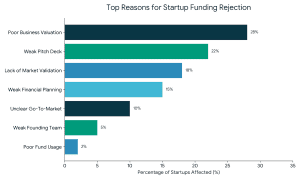
 2. Weak or Incomplete Pitch Deck
2. Weak or Incomplete Pitch Deck 3. Lack of Market Validation
3. Lack of Market Validation 4. Weak Financial Planning and Projections
4. Weak Financial Planning and Projections 8. Not Investor-Ready or Poor Timing
8. Not Investor-Ready or Poor Timing