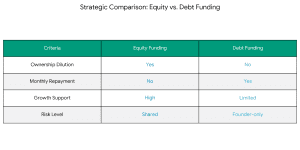
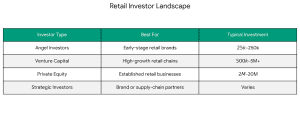
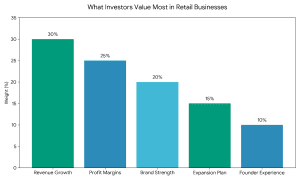
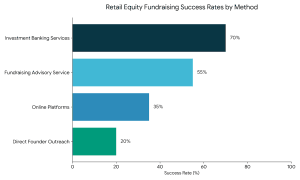
Secure Investment for Your Coaching Institute | EdTech Platform Funding [2026]
Funding for an EdTech platform refers to raising capital from angel investors, venture capital firms, private equity funds, or strategic investors to scale technology, marketing, operations, and student acquisition for an online learning or coaching business in India.
Funding typically ranges from ₹50 lakh (early stage) to ₹100+ crore (growth stage) depending on revenue, traction, and profitability.
Why EdTech Funding in India Is Rebounding in 2026
 The education technology market in India has reached a disciplined development level. Following aggressive growth by competitors such as:
The education technology market in India has reached a disciplined development level. Following aggressive growth by competitors such as:
- Byju’s
- Unacademy
- PhysicsWallah
Traders have ceased to focus on growth at all costs and:
- Profitability
- Sustainable CAC
- Strong retention
- Hybrid learning models
- AI-powered personalization
This opens the doors to serious coaching institutes and the organised online learning start ups.
How Much Funding Can an EdTech Startup Raise in India?
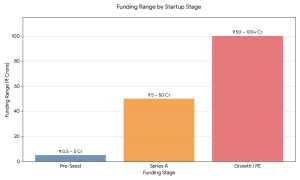 Early Stage (Pre-seed / Seed)
Early Stage (Pre-seed / Seed)
₹50 lakh – ₹5 crore
Focus: MVP, first traction, content creation.
Series A
₹5 crore – ₹50 crore
Focus: Tech + marketing up-scaling.
Growth / PE Stage
₹50 crore – ₹100+ crore
Focus: Growth, buy-overs, profitability.
How Investors Evaluate EdTech Startups (2026 Framework)
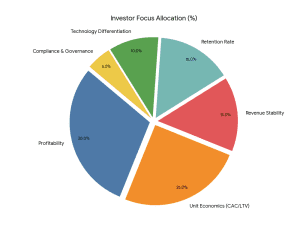 Investors assess:
Investors assess:
- Revenue Model Stability
- Student Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Lifetime Value (LTV)
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR).
- EBITDA Margins
- Retention Rate (More than 60% desirable)
- Technology Differentiation
- Regular compliance in the Securities and Exchange Board of India (structured investments).
How to Calculate Valuation of an EdTech Platform
What Is the Valuation Multiple for EdTech in India?
The EdTech startups usually sell at a multiplier of 3x-8x based on profitability and growth rate. The institutes of coaching that are EBITDA-positive are able to get a higher structured valuation.
Initial estimates can be done using a business valuation calculator – however, institutional investors will need:
- Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis.
- Similar transaction analysis.
- Benchmarking of revenue multiple.
- Cap table structuring
Professional investment banking services guarantee alignment of valuation with the market comparables.
 How to Prepare a Winning Pitch Deck for EdTech Funding
How to Prepare a Winning Pitch Deck for EdTech Funding
A pitch deck with high conversion should have:
- Problem & Market Gap
- Solution & Differentiation
- Market Size (TAM, SAM, SOM)
- Traction Metrics
- Unit Economics
- Revenue Model
- Technology Stack
- Competitive Positioning
- Financial Projections (35 years)
- Fund Utilization
Institutional-grade pitch deck templates enhance clarity and confidence of the investor.
Role of Investment Banking Services in Startup Funding in India
Self-equity raises dilute valuation and slows down the process. Structured investment banking services include:
- Identification of strategic investors.
- Valuation advisory
- Financial modeling
- Term sheet negotiation
- Due diligence management
- Deal closure execution
It usually leads to valuation increase and accelerated funding cycles (3-6 months).
Who Should Raise Funding?
You should consider funding when:
- You are an online-expanding coaching institute.
- You are earning 1 crore and above in a year.
- You are EBITDA positive
- You want to scale nationally
- It is a LMS constructed using AI.
- You plan acquisitions
Step-by-Step Process to Secure EdTech Funding
Step 1: Financial Structuring
Prepare projections, clean financials, audit accounts.
Step 2: Valuation Strategy
Compared to EdTech counterparts in India.
Step 3: Investor Targeting
PE, strategic buyers, Angels, VCs.
Step 4: Data Room Preparation
- Financials
- Cap table
- Compliance documents
- KPI dashboards
Step 5: Term Sheet Negotiation
6: Due Diligence & Fund Closure.
Common Mistakes EdTech Founders Make
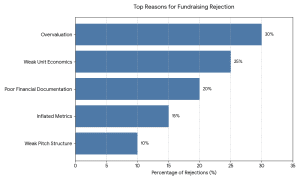
- Overvaluation expectations
- Weak unit economics
- Inflated user metrics
- Poor pitch structure
- There was no distinct roadmap of profitability.
The investors in 2026 are more interested in cash flow discipline than vanity growth.
FAQs – Funding for EdTech Platform
Q. What is the minimum revenue required to raise funding?
No definite qualification exists, but serious investors are attracted to startups with ₹50 lakh and higher annual revenue and good growth rates.
Q. How long does it take to raise startup funding in India?
As short as 360 days in case financial records and pitching materials are available.
Q. Can a coaching institute get private equity funding?
Yes. Potential investors like the private equity are usually interested in profitable coaching institutes with scalable hybrid models.
Q. Is valuation negotiable?
The valuation would be based on the growth rate, profitability, investor demand, and strength of negotiations.
Why 2026 Is the Right Time to Raise EdTech Funding
- Attention to sustainable models by investors.
- Valuation augmented with AI.
- Acquisition exits are formed through consolidation.
- Better regulatory transparency.
India is also among the most dynamic markets in digital education in the world.
Final Strategic Insight
Being investment banking advisors in the education and digital platform business in India, we see that investors have today begun to reward profitability, disciplined growth, and well-organized governance. The founders of EdTech that develop institutional grade financial models and strategy positioning get much more favorable funding conditions.
Ready to Secure Funding for Your EdTech Platform?
Strategic funding is not just capital — it’s valuation optimization, negotiation leverage, and scalable growth positioning. If you’re planning startup funding in India, ensure your financials, valuation strategy, and investor approach are institutionally structured.
Because in 2026 — only disciplined EdTech platforms get premium funding.


 How to Prepare a Winning Pitch Deck for EdTech Funding
How to Prepare a Winning Pitch Deck for EdTech Funding

 Why the Food Sector Attracts Strategic Investors
Why the Food Sector Attracts Strategic Investors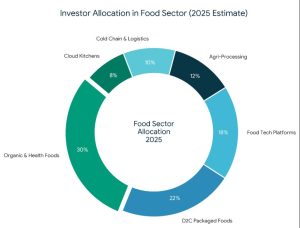 What Is Strategic Funding For The Food Sector?
What Is Strategic Funding For The Food Sector?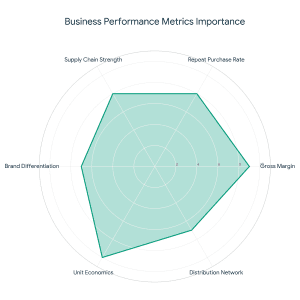 As an adviser to food startups, investors are interested in:
As an adviser to food startups, investors are interested in: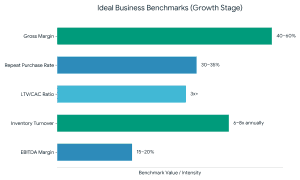 Even the most effective startup fundraising will not work without a powerful grip on these numbers.
Even the most effective startup fundraising will not work without a powerful grip on these numbers.
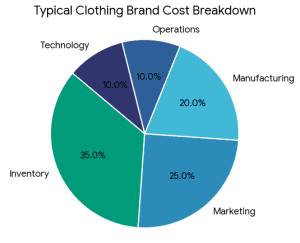 What Is the Best Way to Fund a Clothing Brand?
What Is the Best Way to Fund a Clothing Brand?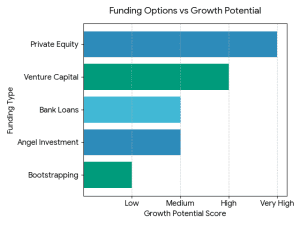 It does not have a single, universal answer. The optimal financing source will be based on:
It does not have a single, universal answer. The optimal financing source will be based on: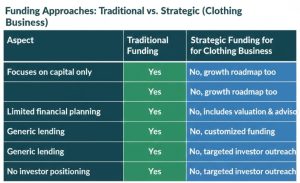
 2. Financial Modeling & Projections
2. Financial Modeling & Projections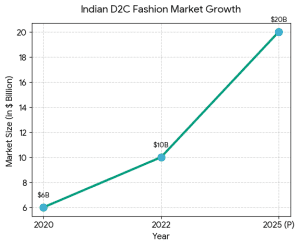 The Indian fashion and D2C market is growing because:
The Indian fashion and D2C market is growing because: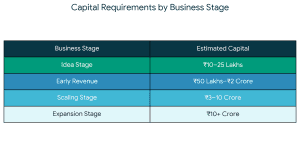
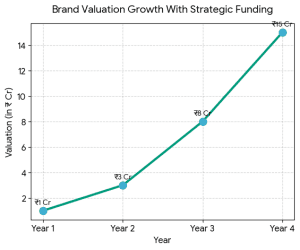
 Why Strategic Funding Is Better Than Just Capital
Why Strategic Funding Is Better Than Just Capital
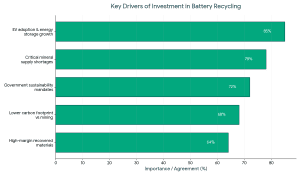 Consequently, the investment in battery recycling startups has taken precedence in clean-tech centric funds and ESG investors, as well as industry actors with a strategic agenda.
Consequently, the investment in battery recycling startups has taken precedence in clean-tech centric funds and ESG investors, as well as industry actors with a strategic agenda.
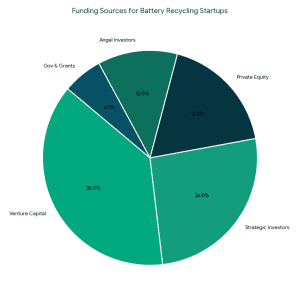 1. Angel Investors for Battery Recycling
1. Angel Investors for Battery Recycling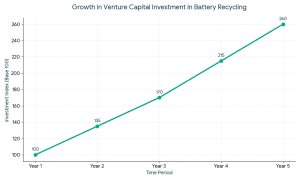 VCs typically invest when:
VCs typically invest when: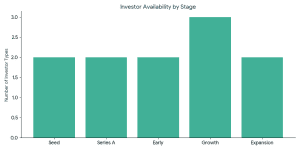 The ideal investors in battery recycling startups usually have the following characteristics:
The ideal investors in battery recycling startups usually have the following characteristics: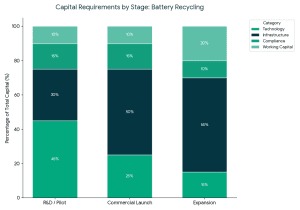 Capital requirements vary by stage:
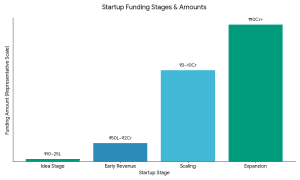
Capital requirements vary by stage:
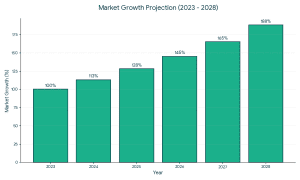 Strong market fundamentals are leading to increased support of organic and clean-label food brands by investors.
Strong market fundamentals are leading to increased support of organic and clean-label food brands by investors.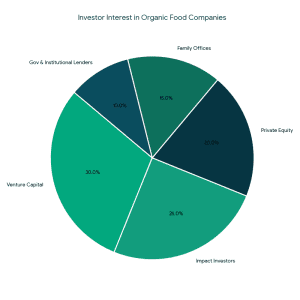 Types of Funding Available for Organic Food Companies
Types of Funding Available for Organic Food Companies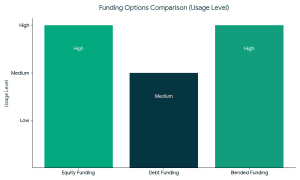 1. Equity Funding
1. Equity Funding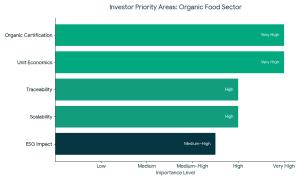 The founders should meet the expectations of the investors to raise funds successfully in organic food companies.
The founders should meet the expectations of the investors to raise funds successfully in organic food companies.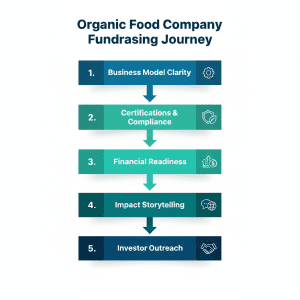 Preparation is the biggest differentiation between funded and unfunded companies.
Preparation is the biggest differentiation between funded and unfunded companies.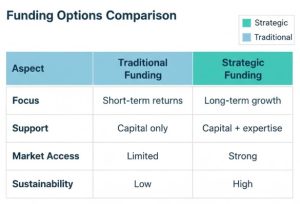 Not all capital is equal.
Not all capital is equal.
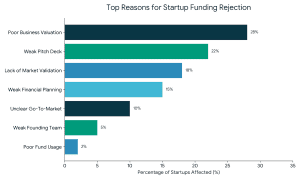
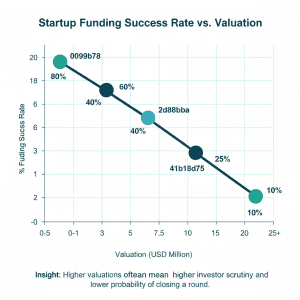 2. Weak or Incomplete Pitch Deck
2. Weak or Incomplete Pitch Deck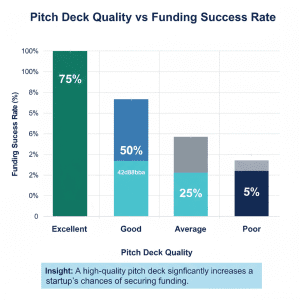 3. Lack of Market Validation
3. Lack of Market Validation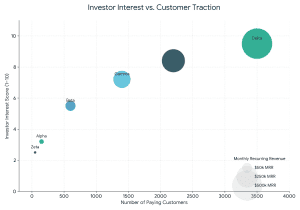 4. Weak Financial Planning and Projections
4. Weak Financial Planning and Projections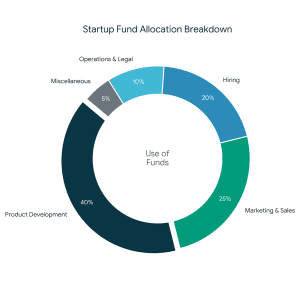 8. Not Investor-Ready or Poor Timing
8. Not Investor-Ready or Poor Timing