Hospital Mergers and Acquisitions: Healthcare M&A Advisory Services & Market Trends (2026)
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in hospitals are transforming the healthcare world faster than ever. Since the merging of the hospital systems to the cross-border mergers and acquisitions in healthcare technology, the transactions are bigger, more intricate and strategic today than in the past. Hospital mergers and acquisitions services are an important factor in this environment to assist hospitals, healthcare companies, and investors make sound and value-driven decisions.

This guide covers the concept of hospital M&A, why expert advisory services are important, and how a properly chosen healthcare M&A advisory firm can make transactions more confident.
What Is Hospital Mergers and Acquisitions?
Hospital mergers and acquisitions are the business deals in which hospitals or healthcare systems merge (mergers) or one of them acquires another (acquisitions). These deals may involve:
- Hospital-to-hospital mergers.
- Speciality clinic acquisitions in the health system.
- Hospital investments through private equity.
- International healthcare deals.
- Healthcare IT, SaaS or technology platform integration.
The main target is to establish sustainable value- financially, operationally, and clinically.
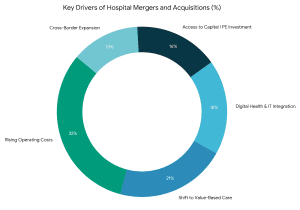
Why Is Hospital M&A Activity Increasing?
There are a number of structural forces in the healthcare industry that are driving the acceleration of hospital M&A:
- Increasing operation expenses and margin pressure.
- Move to value-based care and population health models.
- SaaS and healthcare IT Digital transformation.
- Access to capital due to standalone hospitals.
- International growth of medical care and technology.
The trends have raised the need of specialised hospital M&A advisory healthcare services that are knowledgeable on both financial structuring as well as the healthcare regulations.
What Does a Healthcare M&A Advisory Firm Do?
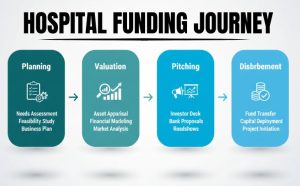
A healthcare M&A advisory firm assists the healthcare organizations with the lifecycle of deals. This is much further than introductions or deal execution.
Basic Healthcare M&A Advisory Services:
1. Strategic Preparedness and Deal Preparation.
Advisers determine the merger and acquisition in line with long-term clinical, financial and growth goals.
2. Valuation of Business and Financing Modeling.
With the help of the sophisticated business valuation software, advisors calculate fair market value taking into consideration the reimbursement risk, payer mix and regulatory factors.

3. Target I.D. & Buyer Outreach.
Established M&A advisory firms in the healthcare industry find strategic buyers, investors, or partners throughout the world.
4. Due Diligence Management
Advisors arrange financial, operational, IT, regulatory, and tax diligence which are essential in a healthcare transaction.
5. Healthcare Deal Advisory M&A and Tax Structuring.
The ability to structure transactions in a manner that maximizes taxation impacts and regulatory controls is necessary more so to nonprofit and cross-border transactions.
6. Negotiation & Transaction Execution.
The advisors safeguard the interests of clients and ensure the best deal value since the letter of intent to closing.
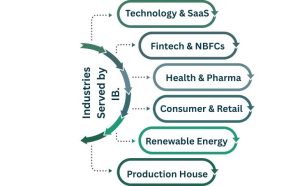
 Specialised Areas Within Healthcare M&A Advisory
Specialised Areas Within Healthcare M&A Advisory
Health care transactions are not equal. The major M&A healthcare advisory firms usually have a vertical focus:
- Hospital & Provider M&A
Specialty providers, community hospitals and health systems. - Healthcare IT M&A Advisory
Includes EHR systems, digital health solutions, and data analytics vendors. - Healthcare SaaS M&A Advisory
Recommends health software in the cloud and subscription-based businesses. - Healthcare Distribution M&A Advisory
Favors mergers in pharma distribution, medical devices and supply chains. - Worldwide Healthcare Technology M&A Advisory.
Leads international transactions on digital health, AI and medtech innovation.
The benefits of having a global healthcare M&A advisory firm are that they have an idea of the international regulations, currency risks, and local market forces.
How Healthcare M&A Advisory Creates Real Value
Senior advisors do not simply make deals, they make things work.
Real-world impact includes:
- Detecting latent synergies within hospital activities.
- Designing transactions that retain clinical independence.
- Avoiding regulatory and compliance traps.
- Enhancing valuation with transparent equity narratives and forecasts.
- Accelerating post-transactions integration.
Several advisory teams also assist clients with free-of-charge pitch deck templates and training on how to tell compelling stories to an investor or buyer.
Hospital M&A vs. General Investment Banking
Traditional Investment Banking Advisory Services can serve M&A in general, but healthcare transactions demand greater industry knowledge.
Healthcare-oriented advisors recognize:
- Antitrust risks and regulatory approvals.
- Dynamics of reimbursement and payers.
- Clinical quality metrics
- IT integration problems in healthcare.
This specialization is particularly relevant in the area of m&a advisory of healthcare firms that work in regulated or technology-driven sectors.
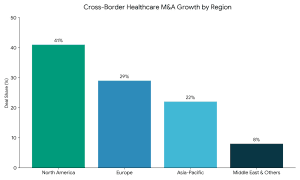
Global Perspective: Healthcare M&A Across Borders
International transactions are increasing at an alarming rate with healthcare technology and services being the main sectors. A healthcare international merger and acquisition advisory firm assists its clients in:
- Laws that are jurisdiction-specific in healthcare.
- International tax structuring.
- Operational integration and cultural integration.
- Expectation of international investors.
This international experience is vital in hospitals and medical firms that want to enjoy size outside their national markets.
Supporting Growth Beyond M&A
The advisory firms that have led in the field usually offer complementary offerings that are conducive to long-term growth, such as:
- Digital health company investment banking services.
- Startup financing in Gurugram and other international innovation centers.
- Healthcare IT and SaaS business capital.
- Platform roll-up and buy-and-build strategic advisory.
These services facilitate that M&A will be part of a larger capital and growth strategy.
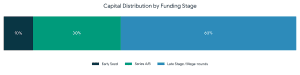
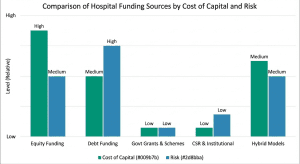
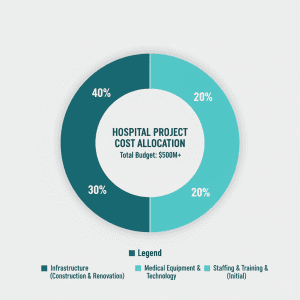
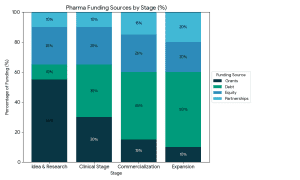
Data Insights: Hospital M&A Market Snapshot
Recent healthcare industry data shows that hospital mergers and acquisitions continue to accelerate as organizations seek scale, cost efficiency, and digital readiness. More than 60% of hospital transactions now involve some form of technology or IT integration, highlighting the strategic role of healthcare SaaS and digital health platforms in modern M&A activity.
Additionally, nearly half of hospital M&A deals involve multi-state or cross-border considerations, making global healthcare M&A advisory expertise increasingly critical.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is healthcare M&A advisory?
Healthcare M&A advisory is an FSR and regulatory counseling of mergers and acquisition in the healthcare sector comprising hospitals, healthcare IT and SaaS firms.
2. Why should hospitals use a healthcare M&A advisory firm?
Hospitals are exposed to special regulatory, operational and financial obstacles. The specialized advisors are useful in dealing with risk, valuation enhancement and good deal outcomes.
3. What is the duration of a hospital M&A transaction?
The average timeframe of the M&A deals is 6-12 months, depending on the complexity of the deal, regulatory approvals, and the level of due diligence.
4. Do cross-border deals best utilize global healthcare M&A advisory firms?
Yes. A medical global M&A consultant firm has experience of international laws, tax planning, and cross-border implementation.
Key Takeaways
- The process of M&A in hospitals is complicated, controlled, and very strategic.
- Advanced healthcare M&A advisory service enhances performance and mitigates risk.
- In healthcare deals, expertise in sectors is more than ever before.
- The need to have global and technology-oriented advisory capabilities is on the rise.
Final Thought
You may be a hospital system looking at consolidation, a healthcare IT company looking at acquisition, or an investor looking at opportunities. You may have the difference between a good deal and a great one in the right healthcare M&A advisory firm. Considerate planning, masterful implementation, and profound industry knowledge have been the core of effective healthcare mergers and acquisitions.


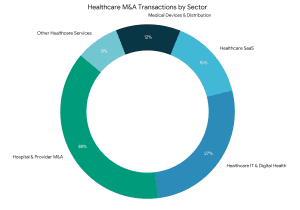 Specialised Areas Within Healthcare M&A Advisory
Specialised Areas Within Healthcare M&A Advisory










 1. Experience
1. Experience

 7 Proven Ways ot Get Funding for Your AI Startup With Zero Connections
7 Proven Ways ot Get Funding for Your AI Startup With Zero Connections 1. Pitch Your Pitch with Free Pitch Deck Templates.
1. Pitch Your Pitch with Free Pitch Deck Templates.